D882 transistor:Introduction, working principle, pin out and data sheet

What is D882 transistor?
D882 transistor is a common NPN transistor, which is widely used in low-power signal amplification, circuit switching and other occasions. It is usually used in audio amplification, switching power supply, current drive and other applications. The following will introduce the pin distribution, working principle and equivalent model of D882 transistor in detail.
D882 transistor technical parameters
Operating voltage:
- Collector-emitter (Vce): up to 50V
- Base-emitter (Vbe): up to 6V
- Collector-base (Vcb): up to 50V
Operating current:
- Collector maximum current (Ic): 150mA
- Base maximum current (Ib): 5mA
Power dissipation: 625mW
Gain (hfe): minimum 100, maximum 300
Maximum junction temperature: 150°C
Package: TO-92
D882 transistor working principle
D882 is an NPN transistor with three main regions: collector, base and emitter. The base region is very thin, usually only a few microns, while the collector and emitter regions have different conductivity. The working principle of the transistor is based on the PN junction behavior of the semiconductor.
Forward Bias: When the voltage across the base (V_BE) relative to the emitter is greater than 0.7V, the base-emitter PN junction is forward biased, allowing base current to flow in. The base current controls the collector current by enhancing the movement of charge carriers (electrons or holes) between the collector and emitter regions.
Reverse Bias: The voltage across the collector (V_CE) is usually maintained at a certain value to ensure that the transistor operates in the amplification region. When the collector voltage is high, the collector-emitter PN junction is reverse biased, which causes most of the current to flow to the collector and very little to flow through the base.
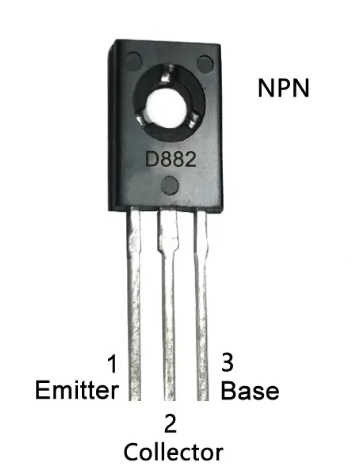
Pinout of D882 Transistor
The D882 transistor is a 3-pin NPN bipolar transistor. Its pinout is as follows:
Pin 1 (C) - Collector
Pin 2 (B) - Base
Pin 3 (E) - Emitter
Equivalent Model of D882 Transistor
In circuit analysis, the equivalent model of the D882 transistor is usually represented by its current gain and voltage characteristics. Its equivalent circuit can be divided into the following parts:
Collector resistance (R_C): represents the impedance of the collector to the emitter current. Usually in circuit design, the collector resistor is used to limit the size of the collector current.
Base current source (I_B): represents the source of the base current. The relationship between the base current and the collector current is determined by the current gain (β) of the transistor. The base current source can be represented by the corresponding current source model.
Collector-emitter diode (D_CE): represents the PN junction between the collector and the emitter. The current-voltage relationship of this diode determines the switching state of the transistor.
Input impedance and output impedance: The input impedance of the D882 transistor is mainly determined by the resistance between the base and the emitter, while the output impedance is determined by the collector current and the collector resistance. In small signal analysis, most of the current source and resistance are usually ignored, and only key parameters such as gain and input/output impedance are concerned.
D882 transistor performance characteristics
High gain:
The gain (hfe) of the D882 ranges from 100 to 300, which is suitable for amplifier circuits that require high gain.
Low saturation voltage:
Wide operating voltage range:
Low noise:
High reliability:
Small package:
D882 transistor application scenarios
Amplifier:
- Audio amplifier: D882 is often used to make preamplifiers and power amplifiers, providing high gain and low noise characteristics.
- Operational amplifier: It can be used as the input stage or intermediate stage of an operational amplifier to improve the overall performance of the amplifier.
Switching circuit:
- Relay drive: D882 can be used as a switch in the relay drive circuit to control the on and off of the relay.
- LED drive: used to drive high-brightness LEDs to control the on and off and brightness of the LEDs.
- Sensor signal amplification: used to amplify the weak signal output by the sensor and improve the signal-to-noise ratio.
- Signal conditioning: used for signal filtering, shaping and amplification to improve the quality of the signal.
Power management:
- Voltage regulator circuit: can be used as an adjustment tube in a linear regulator to provide a stable output voltage.
- Current source: used to build a constant current source circuit to provide a stable current output.
Communication equipment:
- Modem: used for signal amplification and processing in modems.
- Wireless communication: used for signal amplification and modulation in wireless communication equipment.
D882 transistor Equivalents
Based on the performance characteristics of D882, the following are some common equivalent transistors that can usually be used as its replacement:
1. 2N2222
Type: NPN
Maximum collector voltage (V_CEO): 40V
Maximum collector current (I_C): 800mA
Current gain (hFE): 100 to 300
Package type: TO-92
Description: 2N2222 is a classic NPN small signal transistor widely used in low power amplification and switching applications. Although its maximum collector voltage is slightly lower than that of D882, its collector current handling capability is stronger and it can usually be used as a replacement for most low power applications.
2. 2N3904
Type: NPNMaximum Collector Voltage (V_CEO): 40V
Maximum Collector Current (I_C): 200mA
Current Gain (hFE): 100 to 300
Package Type: TO-92
Description: 2N3904 is a common small signal transistor suitable for low power amplifier and switching circuits. Its voltage and current carrying capacity are slightly lower than D882, but they can be used interchangeably in many applications.
3. BC337
Type: NPNMaximum Collector Voltage (V_CEO): 45V
Maximum Collector Current (I_C): 800mA
Current Gain (hFE): 110 to 800
Package Type: TO-92
Description: BC337 is a medium power NPN transistor with high current gain, suitable for amplifier and switching circuits. Its collector current capability and current gain are better than D882, so it can also be used as a substitute.
4. S8050
Type: NPNMaximum collector voltage (V_CEO): 45V
Maximum collector current (I_C): 1A
Current gain (hFE): 100 to 400
Package type: TO-92
Description: The S8050 is a small signal NPN transistor with high current carrying capacity, commonly used in low power applications. Its collector current capability is stronger, suitable for circuits that require higher load driving capabilities.
5. 2N5551
Type: NPNMaximum collector voltage (V_CEO): 60V
Maximum collector current (I_C): 800mA
Current gain (hFE): 200 to 900
Package type: TO-92
Description: The 2N5551 is another NPN transistor suitable for low to medium power applications. Its higher collector voltage and current gain make it suitable for various low power amplification and switching circuits, and can be used as a replacement for the D882.
6. BC547
Type: NPNMaximum Collector Voltage (V_CEO): 45V
Maximum Collector Current (I_C): 100mA
Current Gain (hFE): 110 to 800
Package Type: TO-92
Description: The BC547 is a commonly used small-signal NPN transistor suitable for use in low-voltage, low-power applications. Due to its lower collector current and current gain, it is often used in scenarios such as signal amplification.
How to Choose the Right Equivalent?
Current and Voltage Requirements: Make sure the maximum collector voltage (V_CEO) and maximum collector current (I_C) of the replacement transistor meet the requirements of the circuit. If the circuit requires a larger current carrying capacity, you can choose, for example, 2N2222 or S8050.
Current Gain (hFE): For amplification applications, the current gain of the transistor is very important. Make sure the current gain of the replacement is similar to that of the D882 to avoid unstable performance due to gain differences.
Package Type: If the original circuit uses a TO-92 packaged D882, you need to make sure the replacement also uses the same package type for direct replacement.
Power Dissipation: Although the maximum power dissipation of the D882 is 500mW, you should ensure that its power handling capability is sufficient when selecting a replacement. Generally, 2N2222 and 2N3904 can meet this requirement.
D882 Transistor Datasheet
Click to view the table:
FAQs
What is a D882 transistor?
What is the pinout of D882?
Answer: The D882 transistor is a 3-pin NPN transistor, and the specific pinout is:
Pin 1: Collector (C)
Pin 2: Base (B)
Pin 3: Emitter (E)
What is the maximum current and voltage of the D882 transistor?
Answer: The main electrical characteristics of the D882 transistor are as follows:
Maximum collector voltage (V_CEO): 50V
Maximum collector current (I_C): 150mA
Maximum power dissipation: 500mW
Can D882 and 2N2222 be used interchangeably?
Answer: In many applications, D882 and 2N2222 can be used interchangeably. They are both NPN transistors, but it should be noted that the maximum collector current of 2N2222 (800mA) is higher than that of D882 (150mA), so if the current demand is large, 2N2222 is a better choice.
What is the current gain of D882?
Answer: The current gain (hFE) of D882 is between 100 and 320, depending on the operating conditions. The higher gain value makes it suitable for small signal amplification and driving applications.
How to test the working state of D882 transistor?
Answer: To test the working state of D882 transistor, you can use a multimeter to perform a base voltage test. When the base voltage (V_BE) is greater than 0.7V, the base-emitter PN junction is forward biased and the transistor enters the amplification state. You can use a multimeter to measure the collector current (I_C) and base current (I_B) to verify whether the current gain meets the specifications.
What applications are suitable for D882 transistors?
What are the common substitutes for D882?
2N2222: Suitable for small signal amplification and switching circuits.
2N3904: Slightly lower current and voltage, suitable for lower power applications.
BC337: Has higher current gain and current carrying capacity, suitable for medium power applications.
S8050: Strong current carrying capacity, suitable for applications requiring high current drive.
Summary
D882 is a common NPN transistor suitable for a variety of low-power applications. With its simple three-pin structure, users can easily integrate it into a variety of electronic circuits. Understanding the pin distribution, working principle and equivalent model of D882 will help to give full play to its performance advantages when designing circuits. Whether in audio amplification, switching power supply, or current drive circuits, the D882 is a very reliable and economical choice.
Statement: All articles (images, texts, audio) on this site are uploaded and shared by users, or integrated from relevant internet sources, only for user's learning. If your rights are violated, please contact the administrator to delete! Link to this article: https://www.jinftry.com







