How to Read 47k ohm Resistor Color Code?

What is a 47k Ohm Resistor?
A 47k ohm resistor is a common component in electronic circuits. The term "47k ohms" refers to the resistor's resistance value of 47,000 ohms. Resistors are essential for controlling the flow of electric current in a circuit, ensuring that other components receive the appropriate voltage and current levels.

What is the Color Code 4 Band on a 47k Resistor?
Resistors can come with different color codes to indicate their resistance value. For a 47k ohm resistor with a 4-band color code, the colors typically represent:
First Band: Yellow (4)
Second Band: Violet (7)
Third Band: Brown (multiplier of 10)
Fourth Band: Gold or Silver (tolerance)
Below is a typical 47K ohms resistor with 5% tolerance:

|
Color |
Digit |
Multiplier |
Tolerance |
|
Yellow |
4 |
10^0 |
/ |
|
Violet |
7 |
10^1 |
/ |
|
Brown |
/ |
10^3 |
/ |
|
Gold/Silver |
/ |
/ |
5% |
Here's how it works:
1. Yellow and Violet represent the digits 4 and 7.
2. Brown as the multiplier means you multiply 47 by 10,000, which gives you 470,000 ohms.
3. The Gold or Silver band indicates tolerance, which tells you how much the actual resistance can vary from the nominal value.
How to Read a 4-Band 47k Ohm Resistor Color Code?
To determine the resistance value of a 47k ohm resistor using its color code, follow these steps:
1. Identify the First Digit
The color of the first band represents the first significant digit. For a 47k ohm resistor, this band is Yellow, which corresponds to the digit 4.
2. Identify the Second Digit
The color of the second band represents the second significant digit. For this resistor, the second band is Violet, which corresponds to the digit 7. This gives us the combined digits 47.
3. Determine the Multiplier
The third band shows the multiplier, which scales the combined digits. The color of this band is Orange, which corresponds to a multiplier of 103 (or 1000). Therefore, you multiply the digits 47 by 1000.
4. Calculate the Resistance Value
Multiply the combined digits (47) by the multiplier (1000) to get the total resistance. Thus, 47×1000=47,000 ohms, or 47k ohms.
5. Check the Tolerance
The fourth band indicates the tolerance of the resistor. In this case, the band is Gold, representing a tolerance of ±5%. This means the actual resistance can vary by 5% from the nominal value of 47k ohms.
If you want to measure the color code of other resistors besides 47k ohm resistor color code, you can use calculator tool like Resistor Color Code Calculator, which will help you to identify the color code of resistors accurately and quickly.
What is the Difference Between 4.7k and 47k?
The primary difference between a 4.7k ohm and a 47k ohm resistor lies in their resistance values and how they affect the circuit in which they are used. Here's a comprehensive overview of the differences:
Resistance value
A 4.7k ohm resistor has a resistance of 4,700 ohms, while a 47k ohm resistor has a resistance of 47,000 ohms. This tenfold difference means that the 47k ohm resistor restricts current flow more than the 4.7k ohm resistor.
Current flow
Current flow through a resistor can be calculated using Ohm's Law: I=V/R, where I means Current, V is voltage and R is resistance. Let’s take an example of 5V power supply:
l 4.7Ohms

l 47Ohms
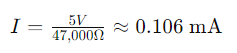
Thus, a 4.7k ohm resistor allows approximately 10 times more current to flow compared to a 47k ohm resistor when both are subjected to the same voltage.
Power dissipation
The 4.7k ohm resistor, due to its lower resistance, will dissipate more power when a current flows through it compared to the 47k ohm resistor. This means that the 4.7k ohm resistor needs to be rated for higher power dissipation to avoid overheating. Conversely, the 47k ohm resistor, with its higher resistance, dissipates less power.
Noise considerations
Lower resistance values, like 4.7k ohms, can generate more thermal noise due to higher current flow. This might affect sensitive circuits. The higher resistance of the 47k ohm resistor typically produces less noise, making it suitable for low-noise applications.
Used fields
The 4.7k ohm resistor is often used in circuits where a moderate current is required. It's commonly found in pull-up/pull-down configurations, signal conditioning, and voltage divider circuits. In contrast, the 47k ohm resistor is used in applications that require higher resistance, such as biasing transistors, high-impedance inputs, and feedback networks in operational amplifiers.
How to Tell if a Resistor is Bad?
Determining whether a resistor is bad involves a few straightforward steps, each focusing on different aspects of its performance and condition. Here’s how to identify a faulty resistor:
1. Measure the Resistance
The most direct method to check if a resistor is bad is to measure its resistance using a digital multimeter (DMM). Set the multimeter to the resistance (ohm) measurement mode and place the probes on each end of the resistor. Compare the measured resistance to the resistor's rated value. For instance, if you have a 10k ohm resistor and it reads significantly higher or lower than 10k ohms, it might be defective. Additionally, make sure the measured resistance falls within the resistor’s tolerance range, which is usually indicated by its color bands. If the value is out of range, the resistor may be faulty.
2. Inspect for Physical Damage
Perform a visual inspection of the resistor for any signs of physical damage. Look for cracks, burns, or discoloration on the resistor’s body. Physical damage often indicates that the resistor has failed or is no longer functioning correctly. For instance, if you see blackened or charred areas, this is a clear sign that the resistor has been subjected to excessive current and may need replacement. Also, check if the resistor has changed shape, such as swelling or bulging, which can also signify a failure.
3. Test the Resistor in Circuit
Testing a resistor in-circuit can provide additional clues, although it's best to power down the circuit first to avoid incorrect readings. Measure the resistance with the multimeter while the resistor is still in the circuit. If the reading deviates significantly from the expected value, it may indicate a problem. However, keep in mind that other components in the circuit can affect the measurement, so this method is less precise compared to testing the resistor out of the circuit.
4. Look for Symptoms of Failure
Observe the circuit’s behavior where the resistor is used. If the circuit isn’t functioning as expected—such as an LED not lighting up properly or a voltage divider not providing the correct voltage—the resistor might be at fault. Additionally, check if the resistor is overheating. Resistors are designed to handle a specific amount of power; excessive heat can be a sign of excessive current or a failing component. If the resistor feels unusually hot to the touch, it could be an indication that it is malfunctioning.
Applications of a 47k Ohm Resistor
1. Voltage Divider Circuits
A 47k ohm resistor is frequently used in voltage divider circuits. These circuits are designed to produce a specific output voltage that is a fraction of the input voltage. By combining a 47k ohm resistor with another resistor of known value, you can create precise voltage levels required for various parts of a circuit. For instance, in a voltage divider setup, the 47k resistor helps scale down voltages to levels suitable for analog-to-digital conversion.
2. Pull-Up and Pull-Down Resistors
In digital circuits, 47k ohm resistors are commonly used as pull-up or pull-down resistors.
Pull-Up Resistors: These resistors ensure that an input pin of a digital device reads a high logic level when not actively driven to a low level. By connecting a 47k ohm resistor between the input pin and the supply voltage, you keep the input at a high state.
Pull-Down Resistors: Conversely, pull-down resistors keep an input pin at a low logic level when no active signal is present. Connecting a 47k ohm resistor between the input pin and ground ensures that the pin remains in a low state.
3. Signal Filtering
47k ohm resistors are also used in signal filtering applications, such as in RC (resistor-capacitor) filters. In these circuits, the 47k resistor works with capacitors to filter out unwanted noise or smooth out signal waveforms. For example, in a low-pass filter, a 47k ohm resistor can help remove high-frequency noise from a signal, allowing only the desired low-frequency components to pass through.
4. Current Limiting
Another crucial application of a 47k ohm resistor is in current-limiting circuits. In such configurations, the resistor limits the amount of current flowing through a particular component, protecting it from damage due to excessive current. For instance, a 47k ohm resistor can be used to limit the current flowing to an LED, ensuring that the LED operates safely without burning out.
5. Biasing Transistors
In transistor circuits, a 47k ohm resistor can be used for biasing purposes. Proper biasing is essential for transistors to function correctly in amplification or switching applications. By using a 47k ohm resistor in the biasing network, you set the correct operating point for the transistor, allowing it to amplify signals or switch states effectively.
6. Feedback Networks
In operational amplifier (op-amp) circuits, a 47k ohm resistor might be used in feedback networks to set gain or stabilize the circuit. For example, in a non-inverting amplifier configuration, the 47k resistor can work with other resistors to define the gain of the amplifier, ensuring accurate signal amplification.
7. Delay Circuits
47k ohm resistors can be used in delay circuits, often in combination with capacitors. These circuits introduce a time delay before a signal reaches its destination. For instance, in a timer circuit, the 47k ohm resistor works with a capacitor to control the timing interval, which can be crucial in various applications such as digital timers or pulse generators.
Understanding resistor color codes and their values is crucial for working with electronic circuits. Whether you're dealing with a 47k ohm or a 4.7k ohm resistor, knowing how to read and measure these components ensures your circuits operate correctly. Welcome to contact Jinftry if you have RFQ.
Related Content:
1. Learn more about 10k ohm resistor color codes
2. How to Read Resistors - Color Codes, Types, Functions
3. 7404 IC: Comprehensive Guide on Datasheet, Pin Diagram, Applications
Statement
All articles (images, texts, audio) on this site are uploaded and shared by users, or integrated from relevant internet sources, only for user's learning. If your rights are violated, please contact the administrator to delete! Link to this article: www.jinftry.com







