What is MOSFET and its working principle and application

Introduction to MOSFET
MOSFET (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor) is an electronic device that controls current by forming a metal oxide layer as a dielectric on a semiconductor. The working principle of MOSFET is based on the control of semiconductor conductivity by electric field. The following is a detailed introduction to the working principle and application of MOSFET:
The working principle of MOSFET:
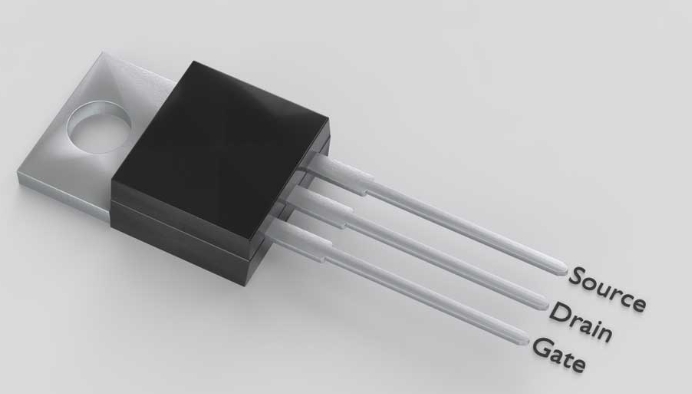
The basic structure of MOSFET consists of three layers: source (SOURCE), drain (DRAIN) and gate (GATE). There is usually a conductive channel made of N-type or P-type material between the source and the drain. The gate is isolated from the conductive channel by an insulating layer (usually silicon dioxide). When voltage is applied between the gate and the source, an electric field is formed on the conductive channel, which controls the conduction or cutoff between the source and the drain.Specifically, when the gate voltage reaches a certain threshold, the conductive channel is formed, and even if there is no voltage between the source and the drain, the channel will have current passing through it. This state is called saturation. If the gate voltage is lower than the threshold, the channel will not form, and almost no current will flow between the source and the drain. This state is called the off state.
MOSFET working state
Off-State:When the gate voltage is low, there are no electrons (N-type MOSFET) or holes (P-type MOSFET) gathered in the channel region, so no conductive path can be formed between the source and the drain, and the MOSFET is in the off state.
On-State:
When a sufficiently high voltage is applied to the gate, the electric field will attract electrons (N-type MOSFET) or holes (P-type MOSFET) to the channel region, thereby forming a conductive channel between the source and the drain. At this time, the MOSFET is turned on and allows current to flow from the source to the drain.
Saturation state:
When the gate voltage is further increased above a certain threshold, the MOSFET enters the saturation state, at which time the gate voltage has little effect on the current, and the current is mainly determined by the applied voltage and the physical properties of the MOSFET.
Charge storage effect:
In practical applications, the channel of the MOSFET may remain in the on state even after the gate voltage is reduced, which is due to the charge storage effect. When the gate voltage is increased and then decreased, some charge may be stored at the interface between the dielectric and the channel, which delays the time when the channel is closed. This phenomenon is called the charge storage effect and has an important impact on the switching performance of the MOSFET.
What are the applications of MOSFET in modern technology
Integrated Circuit (IC) Technology: MOSFET is a key component in the manufacture of integrated circuits, especially CMOS technology, which is used to manufacture almost all modern microprocessors, memory chips and other digital integrated circuits. These chips are widely used in computers, smartphones, consumer electronics and other fields.Power Management: As electronic devices become more complex and portable, the demand for efficient power management is also increasing. MOSFET is widely used in power management and battery management systems due to its low on-resistance and fast switching characteristics, which helps to improve energy efficiency and extend the operating time of devices.
Internet of Things (IoT): IoT devices require miniaturized, low-power electronic components. MOSFET plays an important role in the power management and sensor interface of these devices, supporting connectivity and data transmission functions.
Renewable Energy and Energy Storage: In renewable energy technologies such as solar photovoltaic systems and wind power generation, MOSFET is used for power conversion and management systems. MOSFET also plays a key role in electric vehicles and grid energy storage solutions.
5G and communication technology: With the deployment of 5G networks, the application of MOSFET in RF power amplification, filtering and modulation becomes more important to support higher data transmission rates and network capacity.
High-performance computing and artificial intelligence (AI): High-performance computing systems and data centers use a large number of MOSFETs to build high-speed and efficient processors. At the same time, in the field of artificial intelligence (AI), efficient MOSFET technology helps to achieve more energy-efficient algorithm and hardware design.
Smart home and industrial automation: MOSFET provides precise switching and amplification functions in the control systems of smart home devices and industrial automation, which helps to improve efficiency and reliability.
In the future, as technology advances, MOSFET may further develop to meet the needs of higher performance, lower power consumption and smaller size. Emerging technologies such as quantum computing, photonics integration, bioelectronics, etc. may also bring new opportunities and challenges to the application of MOSFET. Therefore, MOSFET will continue to be one of the important basic components to promote the development of modern science and technology.
Statement: All articles (images, texts, audio) on this site are uploaded and shared by users, or integrated from relevant internet sources, only for user's learning. If your rights are violated, please contact the administrator to delete!
Link to this article: https://www.jinftry.com/